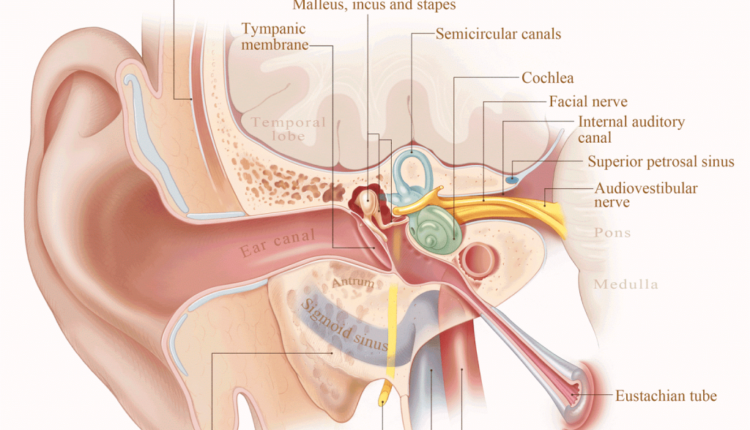
Is mastoiditis occur aftere dental implants
One of the obvious signs of rejection is the movement of the implant. Another symptom is a slight discomfort or pain when pressing on the implant area or when it is tapped. The patient may also experience pain or discomfort on the day of the dental implant placement.
Can you get a bone infection from dental implants?
Sometimes, dental implants can become infected, causing inflammation of the soft tissue and bone loss around the implant, often a condition known as Peri-Implantitis. Peri-implantitis is inflammation similar to the gums and affects the gum tissue and supporting bone surrounding the dental implant.
How do you know if your dental implant is infected? 5 Signs You Have an Implanted Tooth Infection On the same subject : All On Four Dental Implants.
- Pain and Eating Disorders. Having some pain is normal after any invasive dental procedure. …
- Fever, redness, and swelling. …
- A persistent bad taste in your mouth. …
- Bleeding or pus. …
- A flexible tool
Can a dental implant cause osteomyelitis?
Implant surgery has become widespread but remains a spinal surgery that can lead to serious infectious complications, including osteomyelitis. This may interest you : What type of seadtion is recommended for dental implants.
Are infections common after dental implants?
Conclusions: Four to 10% of dental implant patients develop postoperative infections. This problem is important because the applied treatment is usually ineffective and two-thirds of infected implants fail, often before the prosthetic is removed.
Can dental work cause Osteomyelitis?
Osteoporosis is a serious bone infection that can be caused by poor health habits. It can also result from the dentist performing certain procedures in the mouth of a person taking certain medications (bisphosphonates) after cancer or osteoporosis treatment.
How common is dental implant infection?
Conclusions: Four to 10% of dental implant patients develop postoperative infections. See the article : Dentist Teeth Choice. This problem is important because the applied treatment is usually ineffective and two-thirds of infected implants fail, often before the prosthetic is removed.
Can dental implant infection be cured?
If your symptoms are mild, you may be able to get off the antibiotic treatment and continue good oral hygiene with an antiseptic mouthwash. In cases where symptoms worsen, you may need to have the implant removed completely so that the infection can heal properly.
What happens if a tooth implant gets infected?
When the infection attacks the bone, the bone begins to deteriorate. Therefore, the implant loses its base of support and may begin to feel loose. In severe cases, the infection can sneak into the bloodstream and cause systemic health issues. Surgical intervention is often necessary to treat peri-implantitis.
Is infection common after dental implant?
Results: The patient-based prevalence of postoperative infections after implantation was 2.80% (95% confidence interval (95% CI): 2.04% to 3.83%). Thirty-three out of 37 (89.19%) patients with infection had to be re-operated due to antibiotic failure and 65% of the infections were removed.
Can dental implants cause bacterial infections?
Dental Implant Infection Infection is usually caused by bacteria, which accumulates either immediately after the dental implant procedure or years later and can eventually cause bone loss and graft loss.
How can I prevent infection after dental implant?
Good oral hygiene A strict oral hygiene routine is the recommended way to prevent infection after dental implant surgery. A patient’s oral hygiene routine should consist of gentle brushing twice a day as usual. Regular brushing helps prevent the accumulation of bacteria that cause infection.
How is dental osteomyelitis diagnosed?
Currently, the diagnosis of osteomyelitis is primarily made through panoramic radiography, oral imaging, and clinical diagnostic tests [7]. Among these, this study pays particular attention to the role of X-ray imaging.
How common is osteoporosis of the jaw? Osteomyelitis of the jaw is a rare condition, which has been associated with many systemic diseases including diabetes, autoimmune conditions, malignancies, malnutrition, and immunodeficiency.
What is the most accurate test for osteomyelitis?
The presence of bare bone or a positive bone-to-bone test result is moderately predictive of osteomyelitis. MRI is the most accurate imaging test for diagnosing osteomyelitis.
How is osteomyelitis confirmed?
The gold standard for the diagnosis of osteomyelitis is bone biopsy with histopathologic examination and tissue culture.
What blood test shows osteomyelitis?
How is osteomyelitis diagnosed? After evaluating your symptoms and performing a physical exam, your health care provider may order one or more of these tests: Blood tests: A complete blood count (CBC) checks for signs of infection and inflammation. A blood culture looks for bacteria in your blood.
How does osteomyelitis present clinically?
Osteomyelitis is usually diagnosed clinically based on nonspecific symptoms such as fever, chills, fatigue, lethargy, or irritability. Typical signs of infection, including local pain, swelling, or redness, may also occur and usually disappear within 5-7 days.
What is osteomyelitis caused by?
Most cases of osteomyelitis are caused by staphylococcus bacteria, a type of bacteria that is commonly found on the skin or nose of even healthy individuals.
What is the most common cause of osteomyelitis? Bone infections are usually caused by bacteria. But it can also be caused by fungi or other bacteria. When a person has osteomyelitis: Bacteria or other germs can spread to the skin, muscles, or ligaments next to the bone.
What is the most common bone site of osteomyelitis?
In adults, osteomyelitis usually affects the spine and/or pelvis. However, extremism often involves skin lesions, injuries and surgeries.
Which part of bone does osteomyelitis most commonly starts at?
In adults, the spine is the most common site of hematogenous osteomyelitis, but infection can also occur in the long bones, pelvis, and clavicle. Primary hematogenous osteomyelitis is more common in infants and children, usually occurring in the metaphysis of long bones.
What part of the bones does osteomyelitis affect?
Osteomyelitis is a bone infection caused by bacteria or fungi. It causes painful inflammation of the bone marrow, the soft tissue inside your bones. Without treatment, the inflammation of this bone infection can cut off the blood supply to your bone, causing the bone to die.
What happens if osteomyelitis is not treated?
In general, there is a high risk of complications if osteomyelitis develops after a serious bone injury, or after bone surgery: If the infection is not treated, a ball of pus may develop. bones and surrounding tissues.
What are the long-term effects of osteomyelitis?
Osteoporosis requires long-term care to prevent other complications, including care to prevent the following: Fractures of the affected bone. Slow growth in children (if the infection involves the growth plate) Gangrene infection in the affected area.
Can you live with osteomyelitis?
With treatment, the outcome of acute osteomyelitis is usually good. The outlook is worse in those with long-term osteomyelitis. Symptoms can come and go for years, even with surgery. Amputation may be necessary, especially in people with diabetes or poor circulation.
Does osteomyelitis ever go away?
Osteomyelitis is a painful bone infection. It usually goes away if treated early with antibiotics. Otherwise, it can cause permanent damage.
How long can you have chronic osteomyelitis?
Acute osteomyelitis usually refers to an infection lasting less than 1 month, while chronic osteomyelitis refers to an infection lasting more than 4 weeks.
Can you fully recover from osteomyelitis?
Most people with osteomyelitis recover with treatment. Your prognosis is better the earlier you catch the infection and start treatment. Untreated or chronic infections can permanently damage bones, muscles and tissues.
Are infections common with dental implants?
The good news is that the risk of infection after dental surgery is low, and even treating the infection can be easier if the patient sees a dentist after developing warning signs. Signs of infection include the following: Red or swollen gums at the insertion site.
Is infection common after dental implants? Results: The patient-based prevalence of postoperative infections after implantation was 2.80% (95% confidence interval (95% CI): 2.04% to 3.83%). Thirty-three out of 37 (89.19%) patients with infection had to be re-operated due to antibiotic failure and 65% of the infections were removed.
What happens if an implant gets infected?
When the infection attacks the bone, the bone begins to deteriorate. Therefore, the implant loses its base of support and may begin to feel loose. In severe cases, the infection can sneak into the bloodstream and cause systemic health issues. Surgical intervention is often necessary to treat peri-implantitis.
What should I do if my implant is infected?
If you suspect that you have a dental implant infection, it is very important to seek help from a dentist. The infection won’t get better by waiting and seeing if it goes away. Instead, you will need to see a dentist as soon as you suspect an infection.
How do you know if your implant is infected?
Symptoms of dental implant infection include gums that bleed easily when brushing, tender or swollen gums around the implant and increased pocket depth around the implant.
What does implant infection look like?
Red or swollen gums Red and swollen gums are the main indicators of an infection. If your gums do not appear physically swollen, they may be swollen to the touch.
How do you get rid of an implant infection?
Treatment options may include antibiotics, surgery, laser therapy with surface decontamination, mechanical cleaning, or antimicrobial therapy. Your dentist wants you to be healthy. If you suspect an infected implant, contact your dentist immediately so that proper treatment can be started immediately.
Can dental implant infection be cured?
If your symptoms are mild, you may be able to get off the antibiotic treatment and continue good oral hygiene with an antiseptic mouthwash. In cases where symptoms worsen, you may need to have the implant removed completely so that the infection can heal properly.
What happens when your body rejects an implant?
Redness, swelling, swelling, and bleeding around the injection site is a bad sign after the first few days. Infections can and do occur—especially in smokers, people with autoimmune diseases or diabetes, and those with poor oral hygiene.
What happens when the implant is rejected? This is when the body rejects the implant. Symptoms of rejection include increased pain at the injection site, swelling, fever, and chills. Dental implants in the upper jaw may protrude into the sinus cavity. Trauma to the area around the dental implant may loosen the implant, leading to failure.
What causes body to reject implants?
When your body rejects the implant after the jawbone has completely healed, it is classified as latent rejection. This can happen because of poor post-operative care, poor oral hygiene, or trauma. Post rejection usually occurs a year after the implant surgery.
Is it possible for your body to reject an implant?
When it comes to actual rejection, the rates are even lower because the only reason your body can reject the implant is if you happen to be allergic to titanium, which is what the implant is made of.
How do you know if your body is rejecting the implant?
Some symptoms of an allergic reaction include loss of taste, swelling around the gums, and itching. Acute allergic reactions are a sign of dental implant failure because they indicate that your body is rejecting the implant.
What happens when your body rejects a metal implant?
The clinical presentation of iron-insertion reactions is usually non-specific. Bedridden patients may present with topical dermatitis or rash but also with systemic dermatitis. Swelling, pain, draining sinuses, and swelling at the insertion site can be consistent with infection.
Can your body reject the implant?
According to the International Congress of Oral Implantologists it is rare for your body to reject your dental implants. However, this does not mean that your dental implant will not fail. A successful dental implant is one that is placed in healthy bone and is properly cared for after surgery.
Can you be allergic to a metal implant?
Potential allergic reactions associated with implanted metal include eczema, impaired wound and fracture healing, inflammatory reactions, secretions, pain and tenderness. Nickel, cobalt and chromium appear to be the most common allergens.
Can my body reject a dental implant?
According to the International Congress of Oral Surgeons, it is rare for your body to reject your dental implants. However, this does not mean that your dental implant will not fail. A successful dental implant is one that is placed in healthy bone and is properly cared for after surgery.
How often does the body reject dental implants?
The success rates of dental implants are very high, but about 5 to 10% of dental implants fail shortly after the procedure or even months or years later.
How do you know if your body rejects a tooth implant?
Some symptoms of an allergic reaction include loss of taste, swelling around the gums, and itching. Acute allergic reactions are a sign of dental implant failure because they indicate that your body is rejecting the implant.



Comments are closed.